HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It’s the standard language used to create and design web pages. Think of HTML as the skeleton of a website. It structures the content, such as text, images, and links, so that web browsers like Chrome or Firefox can display them correctly.

Features of HTML
- Tags: HTML uses tags like
<h1>,<p>, and<a>to define different parts of a web page. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets and usually come in pairs (opening and closing tags). - Elements: An element consists of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag. For example,
<p>Hello, world!</p>is a paragraph element. - Attributes: Tags can have attributes that provide additional information. For example,
<a href="https://www.tutorialnexa.in">Tutorial Nexa</a>uses thehrefattribute to specify the link destination. - Structure: HTML documents start with a
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration, followed by<html>,<head>, and<body>tags. The content of the website goes inside the<body>tag. - Linking: HTML can link to other web pages or resources like CSS for styling and JavaScript for interactivity.
Example for Students
Imagine you’re creating a simple web page for your school project. You want to have a heading, a paragraph, and a link to your favorite tutorial website, Tutorial Nexa. Here’s how you could do it in HTML:

What is structure of HTML Document?

Structure of an HTML Document
The structure of an HTML document follows a specific format to ensure that web browsers can correctly interpret and display the content. Here’s a breakdown of the main components of an HTML document:
- Document Type Declaration (
<!DOCTYPE html>): This tells the browser that the document is an HTML5 document. - HTML Tag (
<html>...</html>): This is the root element of an HTML document. All other elements are contained within this tag. - Head Section (
<head>...</head>): This section contains meta-information about the document, such as its title and links to scripts and stylesheets. It does not display content on the web page. - Body Section (
<body>...</body>): This section contains all the content of the web page, such as text, images, links, and other elements that will be displayed to the user.
Example of a Basic HTML Document Structure
Here is an example of a simple HTML document structure:

Breakdown of the Structure
<!DOCTYPE html>:- Declares that this document is an HTML5 document.
<html>...</html>:- The root element that contains all the other elements.
<head>...</head>:<title>My First Web Page</title>: Sets the title of the web page, which appears in the browser tab.<meta charset="UTF-8">: Sets the character encoding for the document.<meta name="description" content="A brief description of my web page">: Provides a description of the web page.<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, web development, tutorial">: Lists keywords relevant to the web page.<meta name="author" content="Your Name">: Specifies the author of the document.<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">: Links to an external CSS file for styling.
<body>...</body>:<h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1>: Creates a large heading on the web page.<p>This is a paragraph of text on my web page.</p>: Creates a paragraph of text.<img src="image.jpg" alt="A descriptive text for the image">: Displays an image with a specified source and alternative text.<a href="https://www.tutorialnexa.in">Visit Tutorial Nexa</a>: Creates a clickable link to another website.
This structure provides a solid foundation for building any HTML document, ensuring that your content is organized and displayed correctly in web browsers.
What is a Tag in HTML?

What is a Tag in HTML?
In HTML, a tag is a keyword enclosed in angle brackets (< >) that defines how the content within it should be displayed on a web page. Tags are the building blocks of HTML, and they usually come in pairs: an opening tag and a closing tag. The closing tag is similar to the opening tag but includes a forward slash (/) before the tag name.
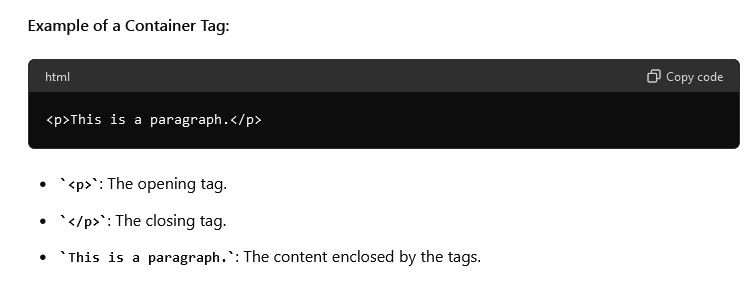
Container Tags
Container tags, also known as paired tags, surround and contain content. They have an opening tag and a closing tag. The content between these tags is affected by the tags’ properties.
Example of a Container Tag:
Empty Tags
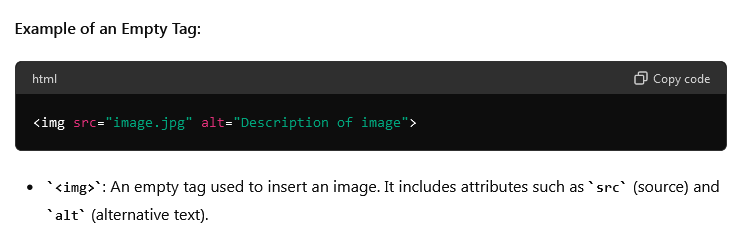
Empty tags, also known as self-closing tags or single tags, do not contain any content and do not have a closing tag. They are used to insert elements that do not need to wrap content, such as line breaks or images.
Example of an Empty Tag:
Summary
- Tag: Keywords in angle brackets used to define elements in an HTML document.
- Container Tags: Tags that enclose content and come in pairs (opening and closing tags). Example:
<p>...</p>. - Empty Tags: Tags that do not enclose content and do not have a closing tag. Example:
<img>,<br>.
Understanding the difference between container and empty tags is fundamental to creating and structuring web pages in HTML.


